Why do some of my users have random numbers attach with their UPN? Well the only answer to this question is, duplication occur because you haven’t force delete the old account from Office 365 recycle bin. And by default there is a setting in Azure AD to detect duplication is set to false, so this is another reason that even there are duplication in AD created and a sync has been trigger the duplication will also be sync to the Office 365.
To prevent any duplication in future to be sync to the Office 365, is to set the duplication checking in Azure AD to true. So that any duplication is scan will be rejected to be sync to the Office 365. To resolve the duplication currently having is to delete the account and resync it to Office 365.
*Note: These random numbers in your smtp has no implication or effects to your mailbox/account, but it is only not nice to see it that way. It is up to your choice to do it or not.
*Azure Module Power Shell needed
- Open Azure power shell
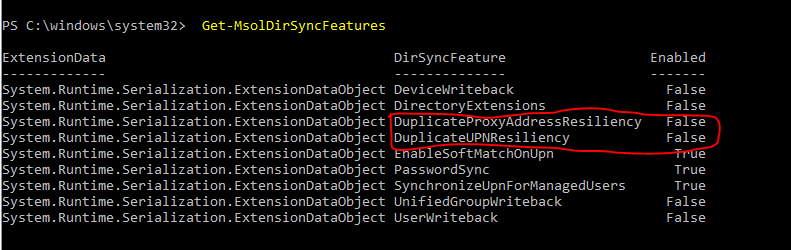
- Type the following command to get the sync feature
Connect-MsolService
Get-MsolDirSyncFeatures
3. Next, enable both of the feature to true
Set-MsolDirSyncFeatures -Feature DuplicateUPNResiliency -Enabled $true
Set-MsolDirSyncFeatures – Feature DuplicateProxyAddressResiliency -Enabled $true
*Note:
Situation 1: If the mailbox is still new, you will only need to delete the account and force delete from the recycle bin, then do a resync
Situation 2: If user have the mailbox for very long, you have to break the dirsync wait for the account’s status change from “Sync from on premise” to “on cloud“, then from Office 365 you can edit its smtp address but make sure you have your recycle bin clear from the old account. (Yes this is much troublesome than Situation 1)
Step by step for situation 1
- Locate the account from Office 356
- Unassign the mailbox license
- At Active Directory, move the account to a unsync organization unit
- At Azure AD Connect, run a manual sync command
Start-ADSyncSyncCycle -PolicyType Delta
5. Make sure the account at Office 365 has gone to the “Deleted User” Category
6. Once the account has been appear in “Deleted User” Office 365, you have to run a command to force deleted from the recycle bin.
7. Open Azure Module PowerShell
8. Type the following command, enter the UPN that you wish to remove from recycle bin
Connect-MsolService
Get-MsolUser -ReturnDeletedUser
Get-MsolUser -ReturnDeletedUser | Remove-MsolUser -UserPrincipalName xxxx@domain.com -RemoveFromRecycleBin -Force
9. After finish remove the account from recycle bin, move back the account from unsync Organization Unit to Sync Organization Unit
10. At Azure AD Connect, run the manual sync command
11. At Office 365, locate the account and assign license
12. You can notice there is no more random numbers found
Step by Step for Situation 2
*Make sure recycle bin is clear from duplication accounts
- Open Azure Module PowerShell
- Type the following command, enter the UPN that you wish to remove from recycle bin
Connect-MsolService
Get-MsolUser -ReturnDeletedUser
Get-MsolUser -ReturnDeletedUser | Remove-MsolUser -UserPrincipalName xxxx@domain.com -RemoveFromRecycleBin -Force
- Open Azure Module Powershell
- Type the following command
Connect-MsolService
Set-MsolDirSyncEnabled -EnableDirSync $false
3. You probably have to wait for 24hr to 48hrs for the dirsync to complete progress
4. At Office 365 > Exchange Online > Recipients > Mailbox
5. Search for the account > Double click on it
6. Go to Email Option > select the smtp address to edit
7. Remove the random numbers from the smtp address
8. Save your changes
*Make sure you put this to lab test before trying it out in actual environment, just to get clear understanding what are you doing
References:
- https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Turn-off-directory-synchronization-for-Office-365-ee5f861e-bd48-4267-83d1-a4ead4b4a00d